 This week was a bit off-week in life science research when we look back at previous ones but still have some interesting minutiae. We can't live in space and keep our skin glowing, mouse model confirmed. Genes lost from y-chromosomes are still in pocket, we didn't know till last week. They are now on autosomes. Talking about DNA, now family of 4 bases is additioned by 2 more bases. Herpes virus, a proved devil, is now proving useful in treatment of skin cancer. Similarly, algae just helped a blind person to see again.
This week was a bit off-week in life science research when we look back at previous ones but still have some interesting minutiae. We can't live in space and keep our skin glowing, mouse model confirmed. Genes lost from y-chromosomes are still in pocket, we didn't know till last week. They are now on autosomes. Talking about DNA, now family of 4 bases is additioned by 2 more bases. Herpes virus, a proved devil, is now proving useful in treatment of skin cancer. Similarly, algae just helped a blind person to see again.
25 - 31 May 2015
![]()
 Space can not save our skin
Space can not save our skin
Study conducted on mice sent on a space mission suggests that weightlessness in space damages skin at the DNA as well as RNA level, interfering with its normal growth cycle. They concluded that similar effects can also be encountered in human astronauts. FInd source
 Y chromosome genes rescued by Autosomes
Y chromosome genes rescued by Autosomes
Loss of genes from the mammalian Y chromosome is not a new theory. However, scientists have now found that many of these genes transfer to autosomes through retro-transposition event. Therefore, it is a rare but vital phenomenon for the preservation of these genes in the genome. FInd source
![]()
 The dark debate of dark chocolate
The dark debate of dark chocolate
A shameful attempt by a science journalist who conducted a false study, claiming dark chocolate helps lose weight, in order to fool reporters. This big headline that appeared on May 27 initiated a serious debate regarding the ethics of journalism in science. Find source
![]()
 Updating the DNA helix with new bases
Updating the DNA helix with new bases
Unlike our primary nucleotide bases, a pair of new bases called Z and P, have been discovered emulating structural properties of DNA’s natural bases. Remarkably, these bases adjust smoothly in the double helix and impart new binding properties for polymerase interaction and protein recognition. Find source
 Herpes virus-an unusual treatment for cancer
Herpes virus-an unusual treatment for cancer
A new type of virus based drugs, called T-vec, are under successful trials in patients with aggressive skin cancer. With a slight modification in the herpes virus genome, scientists have created this unique treatment in which the virus multiplies only inside tumor cells and it will be available this yeat. Find source
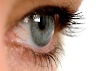 Eye sight restored in blind patients using algae
Eye sight restored in blind patients using algae
Researchers are working on certain protein molecules existing in algae that can transform optic nerve cells in blind patients to respond towards light. This new field of optogenetics can restore vision by targeting retinal cells with defective rods and cones in order to circumvent missing photoreceptors. Find source
 The bigger the better
The bigger the better
Supersized fruits will be available in the market in the forthcoming days. Scientists have done experiments on unspecialized meristematic cells of tomato by stimulating feedback loop genes directly involved in increased cell growth. It is a promising discovery for both plant breeders and eaters. Find source




